Contents
Introduction
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a non-invasive treatment method that has gained significant attention for its effectiveness in treating various mental health conditions. In recent years, “TMS treatment APN” has become a popular search term, reflecting growing interest in this innovative approach.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of TMS treatment APN, focusing on its mechanisms, applications, benefits, and considerations for patients in the United States. We will delve into how TMS works, its potential advantages over traditional treatments, and answer some frequently asked questions to help you make informed decisions about your mental health care.
Understanding TMS Treatment APN
What is TMS Treatment APN?
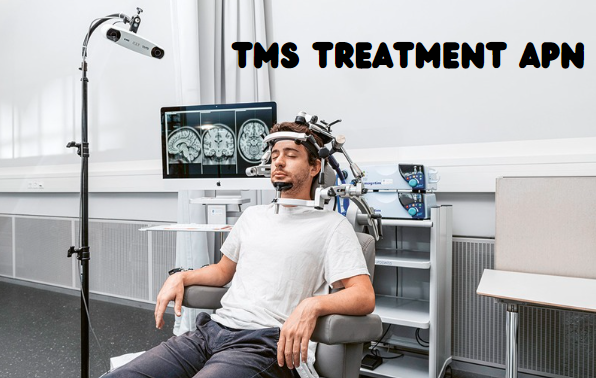
TMS treatment APN refers to the use of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in conjunction with Advanced Practice Nursing (APN) services. TMS is a non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in specific areas of the brain, particularly those associated with mood regulation.
This treatment is primarily used for patients with depression who have not responded well to other treatments like medication or therapy. When paired with APN, which involves highly skilled nurse practitioners specializing in mental health care, TMS can be a powerful tool in managing treatment-resistant conditions.
How Does TMS Treatment APN Work?
TMS treatment APN works by generating magnetic pulses through a coil placed on the scalp. These pulses create small electrical currents in the brain, targeting specific regions like the prefrontal cortex, which is often underactive in individuals with depression. By stimulating these areas, TMS helps to normalize brain activity, which can alleviate symptoms of depression and other mental health disorders.
The involvement of an Advanced Practice Nurse (APN) enhances the treatment process by providing expert care and monitoring throughout the TMS sessions. APNs can assess patient progress, adjust treatment protocols as necessary, and offer comprehensive support, making the treatment more personalized and effective.
The Science Behind TMS
TMS is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When the TMS device is activated, it sends a magnetic pulse through the skull and into the brain. This pulse induces a small electrical current in the targeted brain area, which can modulate the activity of neurons. Repeated sessions of TMS can lead to long-lasting changes in brain function, potentially offering relief from symptoms of depression and other conditions.
Applications of TMS Treatment APN
1. Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
One of the most common applications of TMS treatment APN is in treating Major Depressive Disorder (MDD). Many patients with MDD do not respond adequately to antidepressants or psychotherapy. TMS offers an alternative by directly targeting the brain areas involved in mood regulation. Clinical trials have shown that TMS can significantly reduce depressive symptoms, especially in treatment-resistant cases.
2. Anxiety Disorders
TMS is also being explored as a treatment for various anxiety disorders, including Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). By modulating brain activity, TMS can help reduce the excessive worry and intrusive thoughts that characterize these conditions.
3. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
For individuals with PTSD, TMS treatment APN offers a promising approach. PTSD is associated with hyperactivity in certain brain regions, such as the amygdala, which is involved in fear and emotional processing. TMS can help regulate these areas, potentially reducing symptoms like flashbacks, hypervigilance, and emotional numbness.
4. Chronic Pain
Emerging research suggests that TMS may be effective in managing chronic pain conditions like fibromyalgia and neuropathic pain. By targeting the brain’s pain processing centers, TMS can reduce pain perception and improve the quality of life for patients with chronic pain.
5. Substance Use Disorders
TMS is also being investigated as a treatment for substance use disorders, including addiction to alcohol, nicotine, and other drugs. By affecting brain circuits involved in reward and impulse control, TMS may help reduce cravings and prevent relapse.
Benefits of TMS Treatment APN
1. Non-Invasive and Drug-Free
One of the most significant advantages of TMS treatment APN is that it is non-invasive and does not require medication. This makes it an attractive option for patients who cannot tolerate the side effects of antidepressants or other psychiatric drugs.
2. High Efficacy in Treatment-Resistant Cases
TMS has been particularly effective in patients who have not responded to other treatments. Studies show that TMS can lead to significant improvements in symptoms for individuals with treatment-resistant depression.
3. Minimal Side Effects
TMS is generally well-tolerated, with most patients experiencing only mild side effects, such as headaches or scalp discomfort. These side effects are typically short-lived and resolve shortly after the session.
4. Personalized Treatment
When combined with the expertise of an APN, TMS treatment can be tailored to the specific needs of each patient. APNs can monitor progress, adjust treatment parameters, and provide ongoing support, ensuring a more personalized approach to care.
5. No Anesthesia Required
Unlike electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), another treatment for severe depression, TMS does not require anesthesia. This means that patients can drive themselves to and from treatment sessions and resume normal activities immediately afterward.
6. Long-Lasting Results
Many patients experience long-lasting relief from symptoms after completing a course of TMS treatment APN. While some may require maintenance sessions, the effects of TMS can persist for months or even years.
Considerations and Limitations
1. Cost and Accessibility
TMS treatment can be expensive, and while it is covered by some insurance plans, coverage varies widely. Patients should verify their insurance benefits before starting treatment and explore financing options if necessary.
2. Treatment Duration
A typical course of TMS treatment involves daily sessions for several weeks. Each session lasts about 30 to 40 minutes, which can be time-consuming for some patients. However, the potential benefits often outweigh the inconvenience.
3. Not Suitable for All Patients
TMS is not recommended for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as a history of seizures or metal implants in the head. A thorough medical evaluation by an APN or physician is necessary to determine eligibility for TMS treatment.
4. Variable Response Rates
While TMS is effective for many patients, not everyone responds to the treatment. Some individuals may require additional or alternative therapies to achieve the desired results.
The Role of Advanced Practice Nurses (APNs) in TMS Treatment
1. Expertise in Mental Health
Advanced Practice Nurses specializing in mental health play a crucial role in the success of TMS treatment. Their expertise allows them to assess patients’ mental health needs accurately, monitor progress, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
2. Patient Education and Support
APNs are responsible for educating patients about the TMS process, potential side effects, and what to expect during treatment. They provide ongoing support throughout the treatment course, helping patients navigate any challenges that arise.
3. Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment
APNs closely monitor patients during TMS sessions to ensure safety and efficacy. They can make real-time adjustments to the treatment protocol based on patient feedback and clinical observations.
4. Collaborative Care
APNs often work as part of a multidisciplinary team, collaborating with psychiatrists, psychologists, and other healthcare providers to deliver comprehensive care. This team-based approach enhances the overall quality of treatment and supports holistic patient well-being.
Future Directions for TMS Treatment APN
1. Expanding Indications
As research continues, the range of conditions treated with TMS is likely to expand. Ongoing studies are exploring the use of TMS for conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, bipolar disorder, and even tinnitus.
2. Technological Advancements
Advances in TMS technology are expected to improve the precision and effectiveness of treatment. For example, newer TMS devices may allow for more targeted stimulation or shorter treatment sessions, making the therapy more accessible and convenient.
3. Integration with Digital Health
The integration of TMS with digital health tools, such as telemedicine and wearable devices, could further enhance the treatment experience. Patients may be able to receive TMS in conjunction with remote monitoring and virtual consultations, increasing access to care.
4. Personalized Medicine
The future of TMS treatment APN may involve more personalized approaches, using genetic and biomarker information to tailor treatments to individual patients. This precision medicine approach could improve response rates and reduce the trial-and-error aspect of mental health treatment.
FAQs About TMS Treatment APN
1. What is the success rate of TMS treatment APN?
- The success rate of TMS treatment APN varies depending on the condition being treated and the individual patient. For treatment-resistant depression, studies have shown that about 50-60% of patients experience a significant reduction in symptoms, and about one-third achieve full remission.
2. How long do the effects of TMS last?
- The effects of TMS can last for several months to years. Some patients may require maintenance sessions to sustain the benefits, especially if symptoms start to return.
3. Is TMS treatment APN safe?
- Yes, TMS treatment is generally safe and well-tolerated. The most common side effects are mild and include headaches or scalp discomfort. Serious side effects, such as seizures, are rare but can occur in individuals with certain risk factors.
4. Can I continue taking medication while undergoing TMS treatment?
- In most cases, patients can continue taking their prescribed medications while undergoing TMS treatment. However, it’s essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking, as some may interact with the treatment.
5. How do I know if TMS treatment APN is right for me?
- TMS treatment may be a good option if you have not responded well to other treatments for depression or another mental health condition. A thorough evaluation by a qualified healthcare provider, such as an APN, can help determine if TMS is appropriate for you.
Conclusion
TMS treatment APN represents a promising advancement in the field of mental health care, offering hope to those who have struggled with treatment-resistant conditions. By combining the power of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation with the expertise of Advanced Practice Nurses, this treatment approach provides a non-invasive, effective, and personalized option for patients in the United States.
As research and technology continue to evolve, TMS treatment APN is poised to become an increasingly important tool in the fight against mental illness, offering relief and improved quality of life to countless individuals.